Microbiota transplantation: Targeting cancer treatment
照片为第一作者吴霞
原标题:菌群移植:靶向癌症治疗
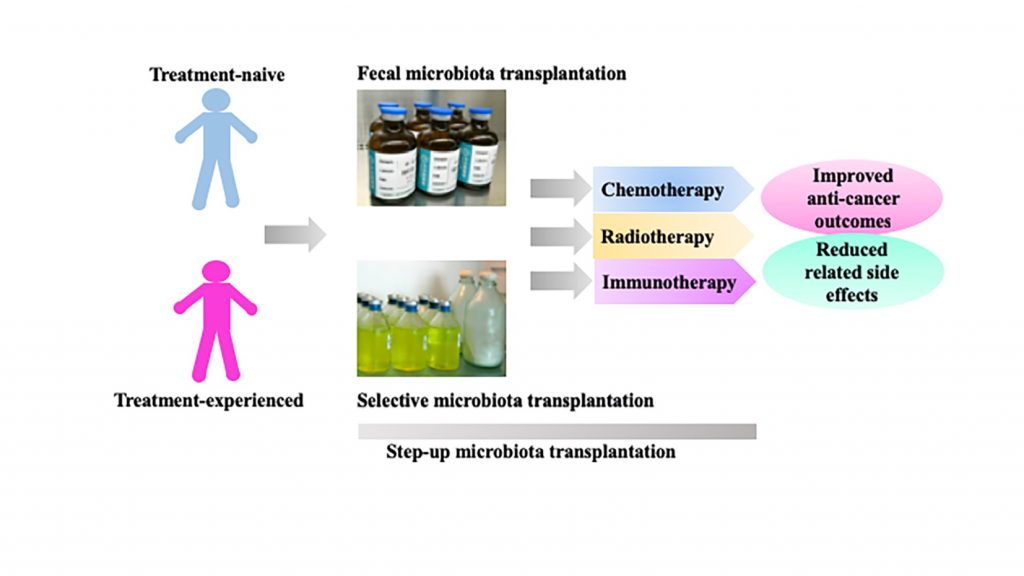
- 肠道菌群移植在抗癌的临床疗效和减轻治疗相关毒副作用方面有重要作用;
- 菌群移植用于消化道途径包括粪菌移植(FMT)和选择性菌群移植(SMT),菌群升阶治疗策略(step-up MT)需要个体化应用;
- 菌群移植用于肿瘤治疗的有效性和安全性是这一转化研究领域的核心问题;
- 基于智能分离系统和独立实验室的“clean FMT”已进入临床应用;
- 结肠途径经内镜肠道植管术(TET)作为新型给药途径,使肿瘤治疗中所需的全结肠途径反复移植成为可能。重视菌群移植应用于肿瘤治疗的有效性和安全性是这一转化研究领域的核心问题;
关键词:肿瘤;化疗;放疗;免疫治疗;菌群移植;结肠途径经内镜肠道植管术(TET)
原文链接:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30905818
Cancer letters [IF:6.491]
Microbiota transplantation: Targeting cancer treatment DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2019.03.010
Abstract:
Mounting evidence have demonstrated that gut microbiota plays a critical role in cancer patients’ therapeutic responses to chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy, including clinical efficacy and sensitivity to toxicity. These fascinating findings evoke a possibility of manipulating gut microbiota to optimize anti-cancer treatment from bench to beside. Microbiota transplantation (MT), including fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) and selective microbiota transplantation (SMT), may improve the effect of anti-cancer treatment and/or reduce the related side effects. The safety and efficacy of MT in cancer treatment are the core of translational research in this promising field, which inspire us to focus on the MT technology and mechanism of MT targeting anti-cancer treatment. To perform clean FMT based on automatic methods by machine in exclusive laboratory has become true. Colonic transendoscopic enteral tubing as a novel delivering way for MT should bring convenience for frequent delivering in practice and feasible tool for confirming the therapeutic effect in research. The present review focuses on the recent findings on role of microbiota on chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy, and the methodology, feasibility and challenges of MT in anti-cancer treatment.
First Author: Xia Wu
Correspondence: Faming Zhang
All Authors: Xia Wu, Ting Zhang, Xiong Chen, Guozhong Ji, Faming Zhang
主编评语:
多项研究发现抗癌治疗的疗效和相关毒副作用与肠道菌群存在密切联系,因此菌群移植有望成为癌症治疗领域的新手段。《Cancer Letters》近期发表来自南京医科大学第二附属医院张发明团队的综述,阐述了菌群和菌群移植在化疗、放疗和免疫治疗中的作用,特别提到了作者团队在菌群移植体系、新型移植途径结肠TET、选择性菌群移植领域的创新。文章全面综述了菌群移植应用于肿瘤治疗的方法学、有效性及挑战,值得品读!


